What is robotic surgery?
Robotic surgery, or robotic-assisted surgery, uses specialized technology to deliver precise care. Robotic surgery is a type of minimally invasive surgery which involves using robotic technology to perform a surgery. When talking about robotic surgery it’s important to define which type of robotic system is being discussed. At Texas Health Center for Diagnostics and Surgery we offer several options for robotic assisted surgery including, the da Vinci, the Mako (for joint replacement) and the AquaBeam Robotic system (for BPH treatment).
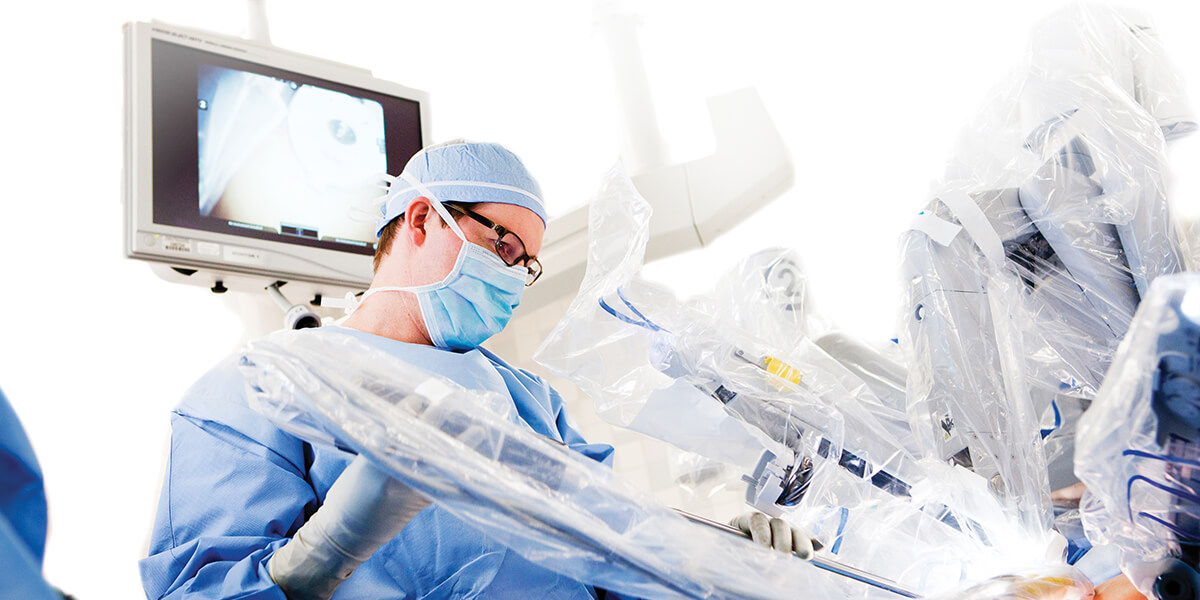
With the DaVinci robotic system, the robot translates the surgeon’s hand, wrist, and finger movements to guide each instrument in real-time. Some patients may be intimidated by the idea of a robot performing surgery. Understand that the robotic surgery system cannot “think” on its own. It can only respond to the surgeon’s precise hand and finger movements. The surgeon is in the operating room throughout the procedure. The robot never makes decision or performs incisions. Rather, the surgeon tells the robot what to do, allowing for greater precision than is possible with the human hand on its own.
What are the types of Robotic Surgery?
THCDS offers robotic-assisted surgery in three key areas: gynecologic, colorectal, urology and general surgery performed by the da Vinci Surgical System; aquablation, a robotic-assisted procedure for treating an enlarged prostate; and robotic orthopedic surgery, including Mako knee replacement surgery.
Da Vinci Surgical System. Surgeons on the medical staff at THCDS employ the da Vinci robotic system -- the world’s most advanced surgical robot – to perform gynecologic and general surgical procedures.
Approved by the FDA for gynecologic surgery in 2005, the da Vinci has been employed in more than 3 million successful surgical procedures.
The da Vinci system enables surgeons to perform minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery through a few small incisions. Seated at a console and viewing a magnified, high-definition 3D monitor, the surgeon controls da Vinci’s four robotic arms with his or her hand motions. Every movement the surgeon makes is replicated precisely by the robot. The console’s design allows the surgeon’s eyes and hands to stay perfectly aligned with his/her view of the surgical site, which minimizes surgeon fatigue.
Utilizing this technology, surgeons can now perform a growing number of complex surgical procedures. The da Vinci Hysterectomy is the #1 minimally invasive hysterectomy performed in the U.S. Other common gynecologic procedures performed with the da Vinci Surgical System include endometriosis resection, myomectomy, sacrocolpopexy, removal of gynecologic malignancies, and procedures to treat uterine prolapse and chronic pelvic pain.
Many general surgical procedures in the abdominal area can be effectively and safely conducted robotically, including hernia repair and bariatric surgery (gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy.)
AquaBeam Robotic System. THCDS also offers aquablation, a non-invasive, robotic-assisted surgery for benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH), more commonly known as an enlarged prostate. Aquablation uses an image-guided robotic arm and requires no incision. The robotic arm wields a water jet to precisely remove excess tissue in the prostate that’s obstructing urine flow.
“Aquablation helps relieve the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) with a much lower chance of procedure-related side effects, as compared to other available surgical treatment options,” said Dr. Michael B. Gross, a urologist on the medical staff of Texas Health Center for Diagnostics and Surgery (THCDS) in Plano, Texas. “It also allows surgeons to operate on patients with very large prostates with more precision, which typically results in less bleeding and much less time in surgery.”
Aquablation offers several advantages over traditional surgical options. By using a multi-dimensional view of the prostate along with a jet of room temperature saline water, delivered with robotic technology, the surgeon can remove the prostate tissue while maintaining low rates of irreversible complications.
The traditional surgical option for very large prostates has been open prostatectomy, which involves incisions made through the abdomen. With aquablation, patients now have a minimally invasive surgery option.
“One of the big advantages of Aquablation is that we can treat a very large prostate that otherwise would require invasive surgery,” said Dr. Gross. “With Aquablation, the procedure typically only requires a few additional minutes for a patient with a larger prostate.”
Mako Knee Replacement Surgery. At THCDS, the Mako robotic system can be employed for knee replacement surgery. With robotic knee surgery (also called robotic knee arthroplasty or robotic total knee replacement), the surgeon resurfaces parts of the joint damaged by arthritis. Metal and plastic parts are used to cap the ends of the bones that form the knee joint, along with the kneecap.
The Mako system gives the surgeon a more detailed view of the joint before and during surgery, enabling more control and consistency.
“Robotic knee replacement surgery uses a computed tomography (CT) scan to allow for operative mapping of implant placement,” according to Dr. J. Conner Ryan, an orthopedic surgeon on the medical staff at Texas Health Center for Diagnostics and Surgery (THCDS). “The robot allows for accurate bony resections [removal of damaged bone] and functional placement of the implant to help improve balancing of the knee.”
What are the benefits of Robotic Surgery?
Each type of robotic surgery offers its own advantages and nuances.
According to Dr. Darrell Robins, a robotic surgeon on the medical staff at THCDS, “In many cases, robotic surgery enables the patient to receive sophisticated treatments with less downtime. Because robotic surgery involves small incisions, patients may benefit from less surgical trauma, minimal scarring, and faster recovery times compared to traditional open surgery. Depending on the type of robotic surgery, patients may also experience less pain during recovery, reduced blood loss and shorter hospital stays.”
Other advantages of robotic surgery may include:
Greater precision: The robotic arm’s movements are more exact than a human hand, with a greater range of motion. In the case of da Vinci – only - the arms rotate instruments in tight spaces in ways that wouldn’t otherwise be possible.
Better visualization: A sophisticated camera provides magnified, high-definition views of the surgical area. It also has 3D capabilities for imaging that are superior to the naked eye.
Darrell Robins, MD, says that better visualization makes all the difference.
“When you look through the console, and you see things in three dimensions and in high definition, it's just incredible,” he said. “While working on the da Vinci system, I can see areas even more clearly that I could if we had opened the patient with a large incision. That allows us to literally accomplish the surgery as if we had the patient open, and we can take on much more challenging cases this way and offer the patient a minimally invasive approach.”
Conclusion
Texas Health Center for Diagnostics and Surgery in Plano offers a range of robotic-assisted surgery options and specially trained surgeons. Follow these links to learn more about Da Vinci Robotic Surgery, Robotic Knee Replacement and other technologies at THCDS. For more information on aquablation, visit this web page.
[1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7714869/
[2] https://www.intuitive.com/en-us/patients/da-vinci-robotic-surgery
[3] https://www.intuitive.com/en-us/patients/da-vinci-robotic-surgery/about-the-systems